Our solar system was formed millions of years ago. More exactly 4.5 billion years. But how did it
originate and how did one get the idea that there is a universe? When did people look at the stars and
believe that the vastness of the universe existed?
In 1755 the German philosopher Kant and the French astronomer Laplace formulated a theory of origin
of our solar system, the principles of which are still correct today. But let's start from the beginning.
About five billion years ago, a huge cloud of gases and dust in our present-day Milky Way slowly

contracted with the help of magnetic forces, electric
currents and gravity. Thus, an increasingly dense core
formed in its center, and as the cloud began to revolve
around this core, it became flatter and flatter. Dust and
gases were drawn into it and whirlpools formed. Due to
an ever increasing pressure of gravitational forces, the
core heated up strongly. More and more matter and
particles joined together to form a solid body, which
orbited the core. In the center an ever increasing heat developed until it reached critical temperatures.
Then a nuclear reaction started and so the fire of the sun was ignited. By the intensive radiation the
sun blew the dust and the gases into the universe. The planets formed there glowed with heat and
huge amounts of meteorites hit, so that the whole surface was provided with craters; likewise also
with the earth.
While the crust of the earth cooled down, inside the embers remained liquid. Still three and a half
billion years ago the earth was an unreal world enveloped by methane, but already at this time the
first life forms developed in the ocean. Between 300 and 400 million years before our time, life had
appeared on Earth.

2000 before Christ there were the first "witnesses" of astronomy.
In Babylonia priests observed the starry sky. They saw gods
in the stars as well as in the planets. Egypt kept measuring its
land because the Nile flooded the fields from time to time.
But there were advantages, and that was that the Nile always left fertile mud behind. Because of the constant measurements,
land surveying and geometry reached an amazing level of
knowledge. In this time astronomy and astrology were still
one and the gods fit into this framework. The surface of the
earth seems to touch the sky in the distance and the sight taught that our point of view
is the center of a circle. Thus was born the statement that the Earth is a disk.
But this theory is shaken when Greek thinkers combine the observational astronomy of the
Babylonians and with the geometrical knowledge of Egypt. For the first time people think about how
the course of the stars (everything that shines in the universe) could come about. In 379 B.C. Platon
mentions in his writing Phaidon that the Earth is spherical and his contemporaries add a rotation to
the sphere by claiming that it rotates. 100 years later, Aristarchus of Samos declares that all fixed stars
are in fact worlds distant from the sun,
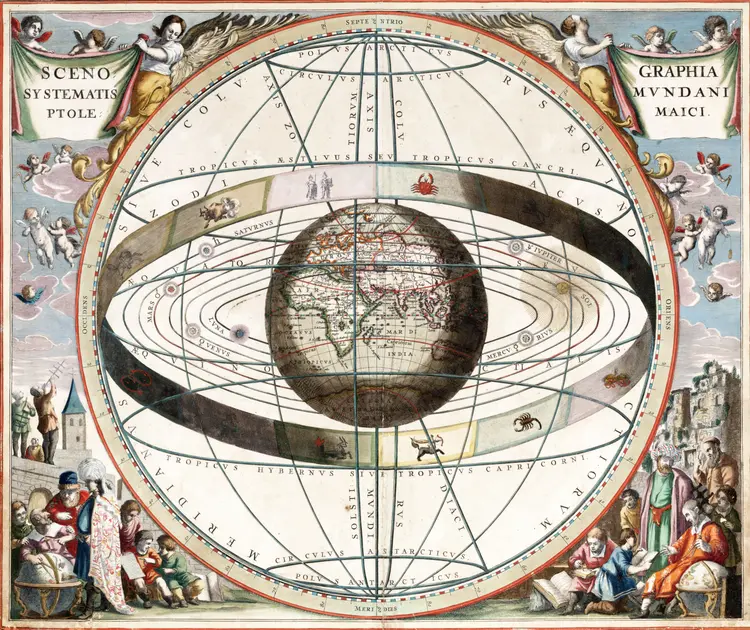
and it is not the earth that is the center, but the sun. However, this way of thinking was too unusual to catch on. This thought was very blasphemous, since everyone thought that the stars were gods. Hipparchus, the great astronomer of this century remained faithful to the old way of thinking and thus the earth was again the center. He also compiled a catalog of over thousands of fixed stars by position and brightness. In the Renaissance around 1500 A.D. Columbus and Magellan sailed through this knowledge towards America and so they discovered the passage through the Pacific Ocean.
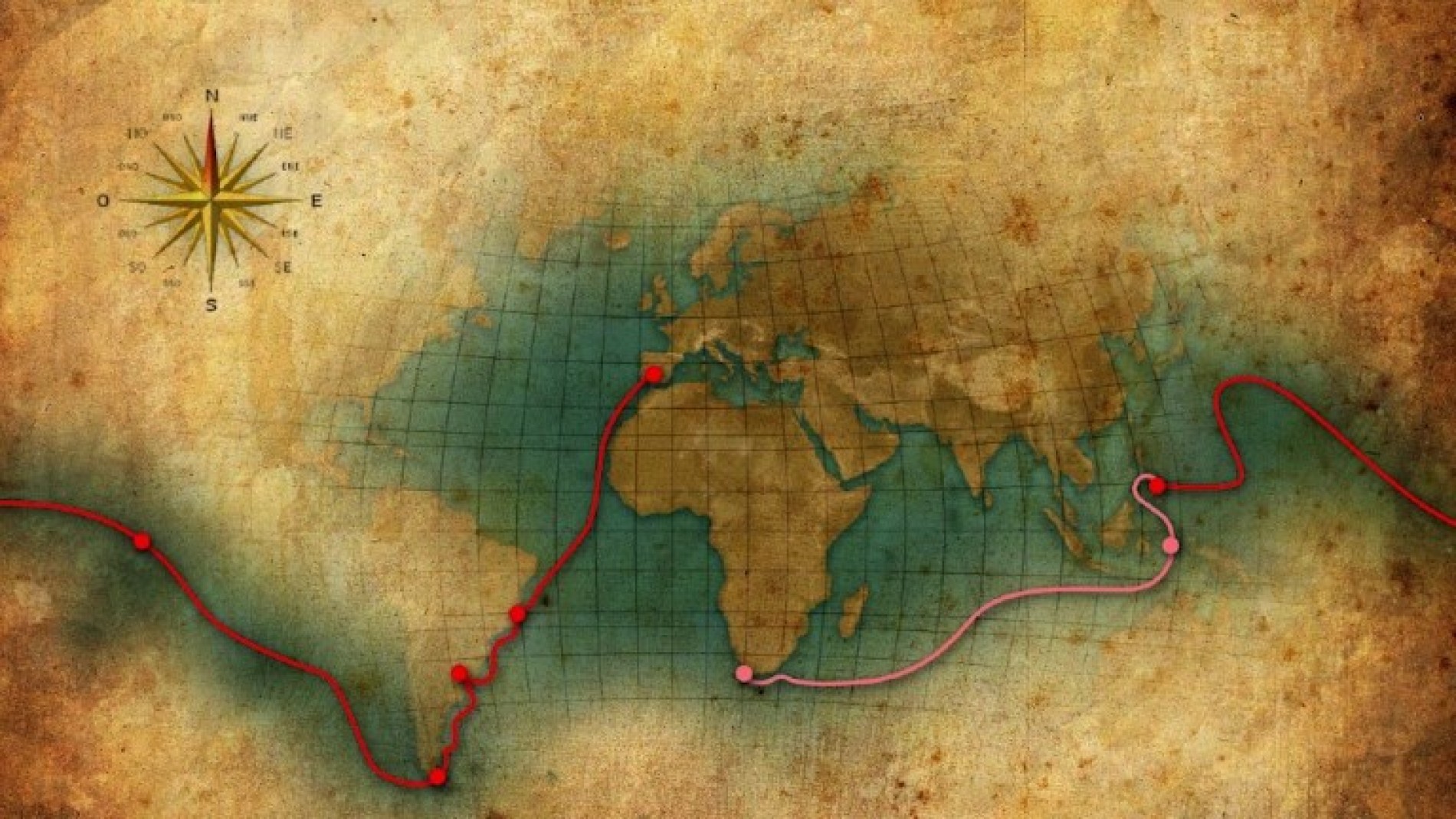
After three years, one of Magellan's ships circumnavigated the
Earth and brought proof of the spherical shape of the Earth. The
year 1543 was the birth year of a new astronomy and the death
year of its founder Nicolaus Copernicus. In this year his 6 books
appeared, which put the sun again in the center. However, many
were still against this way of thinking and denied it.
During this
time, the telescope was invented in Holland and it was realized that the moon was uneven. It was
Galileo Galilei who was the first person to look at the sky and confessed to the teachings of Copernicus

(that the sun is in the center, etc.). But the gods stood in the
way of the new way of thinking and the Roman church,
representative of God on earth, feared for the validity of the
biblical statements. Called before the Holy Inquisition,
Galileo publicly abjured to avoid being burned at the stake
like others who had this new way of thinking. In 1602
Johannes Kepler found the documents about the observations
planet Mars, which he had made for many years. So he described mathematically the orbits of the
planets around the sun. He also found the 3 bases which form the celestial mechanics and shows how
the planets orbit around the sun. 50 years later, Newton found that gravity is responsible for the
planets orbiting the sun.
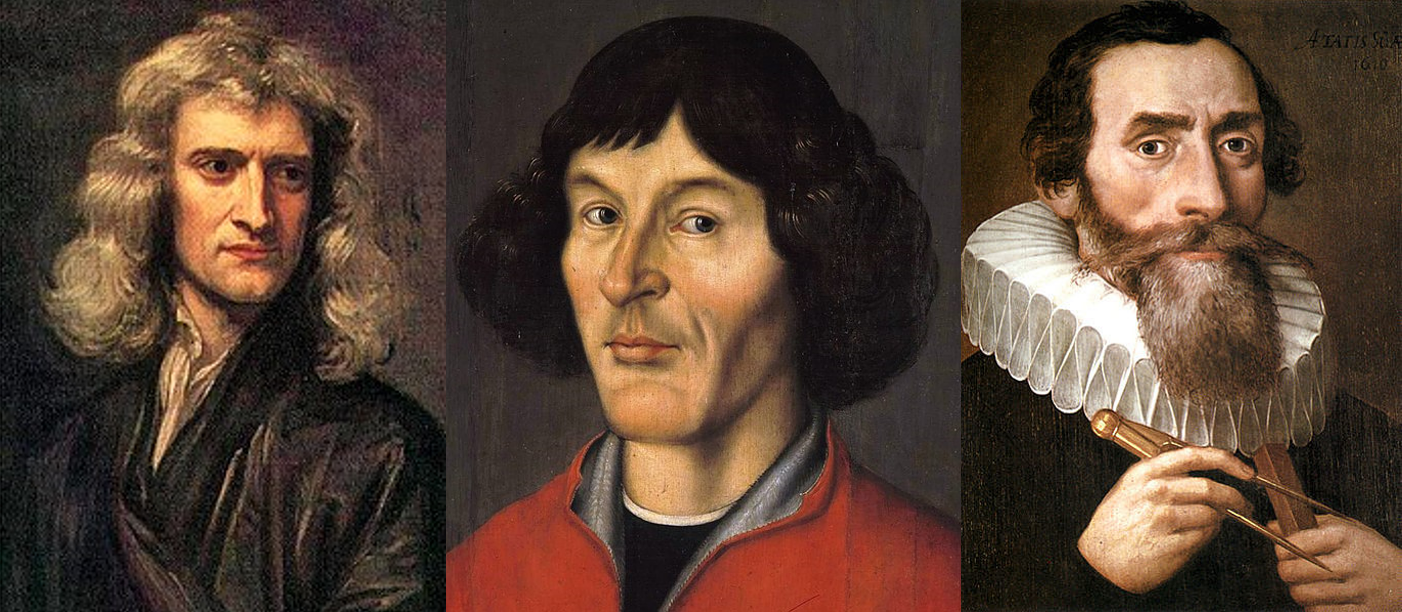
Isaac Newton, Nicolaus Copernicus and Johannes Kepler are the men to whom we owe the discovery
of today's astronomy. After 150 years the theory was also proved that the fixed star parallax exists in
this way. Fixed star parallax is the name of the displacement of a near fixed star against the background
formed by distant stars due to the movement of the Earth on its annual orbit around the Sun.
